OUR RESEARCH AND APPROACH
The research group lead by Neva Caliskan investigates functions and dynamics of RNA molecules in non-canonical translation events, which can affect the interplay between the host and pathogen during infection. Ultimately, they seek to illuminate therapeutic RNA-protein complexes as novel targets to combat infections.
Viruses and cellular genes encode RNAs that can be read in alternative ways during translation, which is called recoding. However, how exactly recoding is regulated by host encoded factors remains elusive. Here, a detailed understanding of recoding and its regulation can open doors for the development of novel RNA-based therapeutic interventions to combat infections.
Neva Caliskan's group investigates the functions and dynamics of RNA molecules and their interplay with trans-acting factors involved in recoding events. They work with several viruses known to depend on recoding strategies for replication including corona and retroviruses, and develop methods to investigate RNA complexes and translation in unprecedented detail.
The group employs a highly interdisciplinary toolset including RNA-antisense purification and mass spectrometry to identify RNA-interaction partners, and cellular assays to investigate molecular details. Ensemble and single molecule assays such as optical tweezers are key to study the dynamics of RNA complexes. Ultimately, they seek to understand how RNA-structure elements act in concert with other factors in the cell to modulate the way mRNA messages are read by ribosomes during infections to advance RNA-based therapeutics.
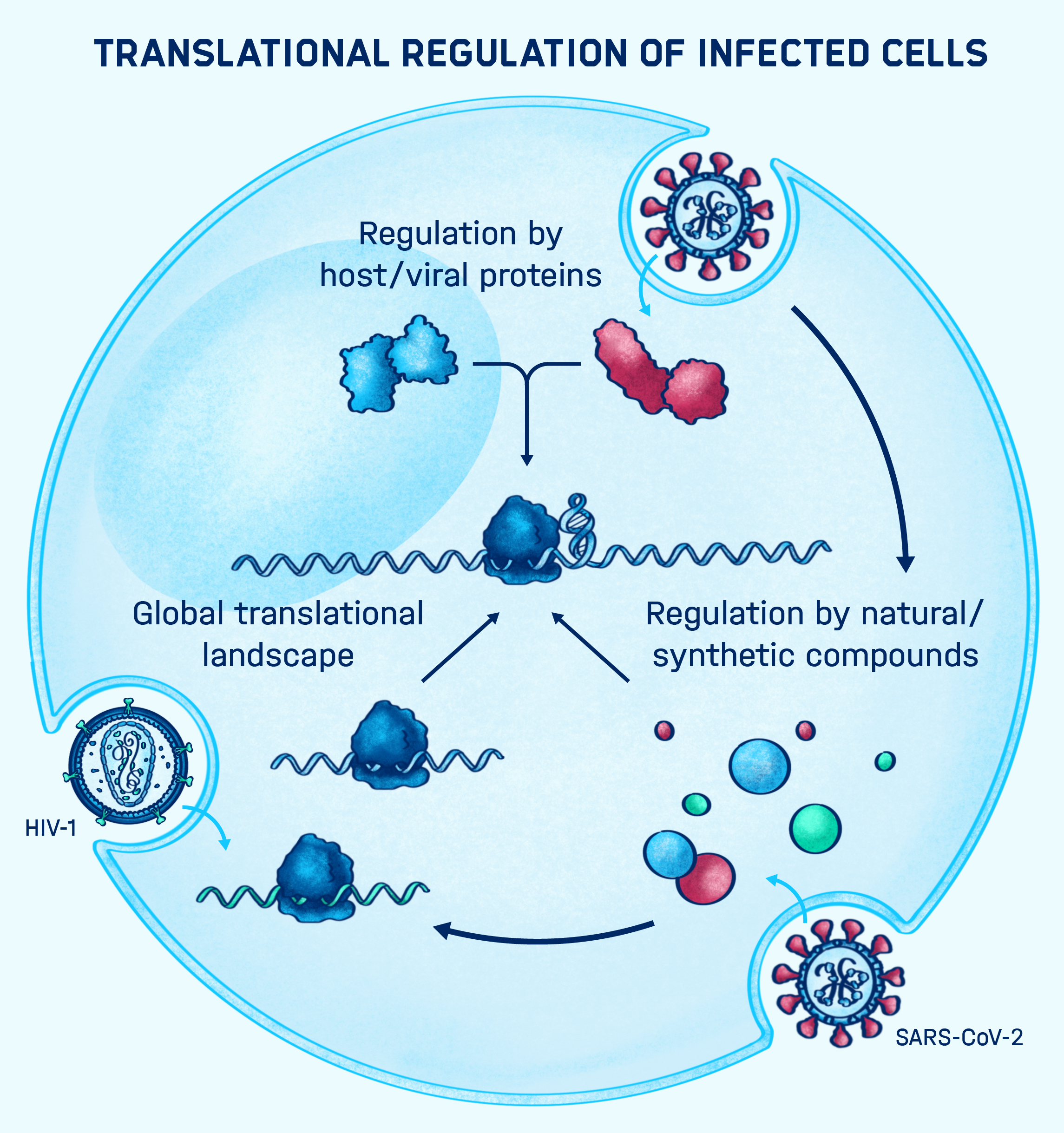

PEERING INTO THE BLACK BOX
Many bacterial and viral pathogens and also their eukaryotic host cells employ non-canonical translation strategies in order to express hidden genes from alternative open reading frames (Caliskan et al., 2015). RNA is a versatile molecule that acts as a key regulator of non-canonical translation events. RNA can exist in various shapes and interact with other regulatory elements such as ncRNAs, small molecules and proteins to alter the meaning of the message encoded in the primary sequence of the mRNA. How RNA structure and regulatory elements drive alternative translation events is currently not fully understood. In addition, it is largely unclear to what extend these translation events are used by the pathogen and the host cell during infections.
We use cutting-edge RNA analytics, such as ribosome profiling and deep sequencing combined with single molecule and computational tools to understand dynamics of translation and the functions of RNA regulators during infections. Ultimately, we want to better understand the interplay between the host's and pathogen's gene expression and harness our knowledge to develop novel therapeutic strategies to combat infectious diseases.
HOW DO VIRUS AND HOST FACTORS MEDIATE RECODING EVENTS?
During infection, viral RNA molecules are expected to interact with the host and viral proteins, which may be critical for the viral replication cycle. Recent examples in cardioviruses (EMCV and TMEV) suggest that frameshifting can be directly mediated by viral 2A protein-RNA interactions. This ensures that the alternative frameshifting product is produced at the right time during infection. Building on this, my group is investigating how viral proteins dynamically interact with structured RNAs and the host translational apparatus during translation.
It is immensely important to gain a better mechanistic understanding of how transfactors control recoding events and alter the mechanical properties of RNA, as modulation of RNA is an effective antiviral strategy.
Our team has recently identified several viral RNA interaction partners that we have shown to interfere with the synthesis of the SARS-CoV-2 polyprotein. We are also currently working on identifying small molecules that can specifically interact with SARS-CoV-2 RNA elements, which we plan to use next for CoV-2 RNA targeting.

HOW RNA CONFORMATION DYNAMICS AND INTERACTIONS DRIVE ALTERNATIVE TRANSLATION EVENTS
RNAs can exist in different forms and interact with other regulatory elements such as ncRNAs, small molecules and proteins to alter the meaning of the message encoded in the primary sequence of the mRNA. How RNA structures and regulatory elements control alternative translation events is not yet fully understood. A key question we are addressing is: "To what extent does the strength of RNA-base pairing interactions and the conformational dynamics of the structure define the propensity of ribosomes to move into an alternative reading frame?" Using state-of-the-art single-molecule and ensemble analysis tools, we investigate how trans-acting factors alter RNA structure. The tools we have developed serve as an entry point for the development of potent and specific modulators of frameshifting.
Publikationen
2024
Translation Inhibition Mediated by Interferon-Stimulated Genes during Viral Infections
Smart A, Gilmer O, Caliskan N (2024)
Viruses 16 (7)
2023
Cis-mediated interactions of the SARS-CoV-2 frameshift RNA alter its conformations and affect function
Pekarek L, Zimmer MM, Gribling-Burrer AS, Buck S, Smyth RP, Caliskan N (2023)
Nucleic Acids Research 51 (2): 728–743
SND1 binds SARS-CoV-2 negative-sense RNA and promotes viral RNA synthesis through NSP9
Schmidt N, Ganskih S, Wei Y, Gabel A, Zielinski S, Keshishian H, Lareau CA, Zimmermann L, Makroczyova J, Pearce C, …, Erhard F, Munschauer M (2023)
Cell 186 (22): 4834-4850.e23
Mouse Liver-Expressed Shiftless Is an Evolutionarily Conserved Antiviral Effector Restricting Human and Murine Hepaciviruses
Zhang Y, Kinast V, Sheldon J, Frericks N, Todt D, Zimmer M, Caliskan N, Brown RJP, Steinmann E, Pietschmann T (2023)
Microbiology Spectrum 11 (4): e0128423
2022
Short- and long-range interactions in the HIV-1 5' UTR regulate genome dimerization and packaging
Ye L, Gribling-Burrer AS, Bohn P, Kibe A, Börtlein C, Ambi UB, Ahmad S, Olguin-Nava M, Smith M, Caliskan N, von Kleist M, Smyth RP (2022)
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology 29 (4): 306-319
Spacer prioritization in CRISPR-Cas9 immunity is enabled by the leader RNA
Liao C, Sharma S, Svensson SL, Kibe A, Weinberg Z, Alkhnbashi OS, Bischler T, Backofen R, Caliskan N, Sharma CM, Beisel CL (2022)
Nature Microbiology 7 (4): 530-541
Editorial: mRNA Translational Control as a Mechanism of Post-transcriptional Gene Regulation
Kiss DL, Vasudevan D, Ho CK, Caliskan N (2022)
Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences 9: 947516
POTATO: Automated pipeline for batch analysis of optical tweezers data
Buck S, Pekarek L, Caliskan N (2022)
Biophysical Journal 121 (15): 2830-2839
Insights from structural studies of the cardiovirus 2A protein
Caliskan N, Hill CH (2022)
Bioscience Reports 42 (1): BSR20210406
Optical Tweezers to Study RNA-Protein Interactions in Translation Regulation
Pekarek L, Buck S, Caliskan N (2022)
Journal of Visualized Experiments (180)
Thinking Outside the Frame: Impacting Genomes Capacity by Programmed Ribosomal Frameshifting
Riegger RJ, Caliskan N (2022)
Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences 9: 842261
2021
Structural and molecular basis for Cardiovirus 2A protein as a viral gene expression switch
Hill CH, Pekarek L, Napthine S, Kibe A, Firth AE, Graham SC, Caliskan N, Brierley I (2021)
Nature Communications 12 (1): 7166
Investigating molecular mechanisms of 2A-stimulated ribosomal pausing and frameshifting in Theilovirus
Hill CH, Cook GM, Napthine S, Kibe A, Brown K, Caliskan N, Firth AE, Graham SC, Brierley I (2021)
Nucleic Acids Research 49 (20): 11938-11958
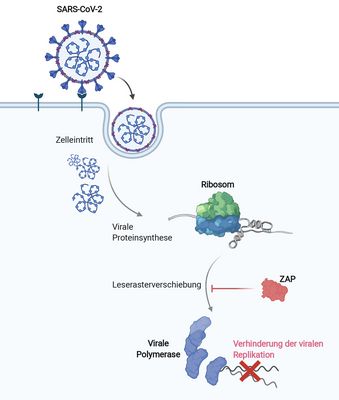
The short isoform of the host antiviral protein ZAP acts as an inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 programmed ribosomal frameshifting
Zimmer MM, Kibe A, Rand U, Pekarek L, Ye L, Buck S, Smyth RP, Cicin-Sain L, Caliskan N (2021)
Nature Communications 12 (1): 7193
2020
The SARS-CoV-2 RNA-protein interactome in infected human cells
Schmidt N, Lareau CA, Keshishian H, Ganskih S, Schneider C, Hennig T, Melanson R, Werner S, Wei Y, Zimmer M, …, Bodem J, Munschauer M (2020)
Nature Microbiology 6 (3): 339-353
2019
Thermodynamic control of -1 programmed ribosomal frameshifting
Bock LV, Caliskan N, Korniy N, Peske F, Rodnina MV, Grubmüller H (2019)
Nature Communications 10: 4598
2018
Small synthetic molecule-stabilized RNA pseudoknot as an activator for -1 ribosomal frameshifting
Matsumoto S, Caliskan N, Rodnina MV, Murata A, Nakatani K (2018)
Nucleic Acids Research 46 (16): 8079-8089
2017
Conditional Switch between Frameshifting Regimes upon Translation of dnaX mRNA
Caliskan N, Wohlgemuth I, Korniy N, Pearson M, Peske F, Rodnina MV (2017)
Molecular Cell 66 (4): 558-567.e4
Aktuelles
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Neuigkeiten aus der Biochemie.

Team Fotos
- All
- Team
- Lab Outing
- Lab






In Focus

GLIMMER OF HOPE IN THE PANDEMIC
ZAP protein inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication by a factor of 20 / Study published in "Nature Communications"
Scientists from Caliskan's research group and other laboratories at HIRI Würzburg and HZI Braunschweig demonstrate for the first time how ZAP, a protein of the human immune defense, inhibits the replication mechanism of the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 and can reduce the viral load by a factor of 20. The findings were published in the journal Nature Communications and could contribute to the development of antiviral agents in the fight against the pandemic.

THE POTATO TOOL: DATA ANALYSIS MADE EASY
Practical Optical Tweezers Analysis Tool
So-called optical tweezers enable the investigation of intra- and intermolecular interactions that control complex biological processes. Recent developments have facilitated data acquisition, but data analysis remains difficult. To enable more efficient data analysis, we have developed the Python-based analysis tool POTATO (Practical Optical Tweezers Analysis Tool). POTATO uses predefined parameters to automatically process raw data. Our research results were presented in the Biophysical Journal.
Team
This is our super great team!

Prof. Dr. Neva Caliskan
Lehrstuhlinhaberin
Pd. Dr. Laura Manelyte
Scientific Staff
Dr. Alexandria Smart
Scientific Staff
PHD Saurav Malik
Scientific Staff
Kristin Hergert
Technical Staff